Speaking of Politics
- Due Process: fair treatment through the judicial system normally gained as a citizen
- Republican Government: political authority is gained through the people but is given to a representative
- Checks and Balances: regulation of an organization by other organization and those are also regulated
- Federalism: form of government that is divided among regions and the national government
- Independent Judiciary: idea that the Judiciary system should distance itself as far from the other branches as possible in order not to be influenced
- Strict Construction: idea that the constitution should be interpreted as time progresses and be more clear on a present day idea
- Loose Construction: idea to understand the constitution in whatever way deems necessary to benefit a certain power like the federal government
- Judicial Review: revision of the constitution to determine whether a act is valid and deemed worthy to be present or not
Preview
- The framers organized it by first giving a citizen the right to protect themselves and their ideas and then they gave them the protection against the law and after the protection of the guilty and then it can be seen that whatever is leftover the years is to be protected even though it is not listed
- The framers gave the executive branch the most power as legislative and judiciary are restriction by the constitution itself
- I feel as though the framers intended to weaken the branches that would seem the strongest and limited them their power
Reading Notes
Section 4.2/4.3
| Constitution | ||
| Preamble | Articles | Amendments |
| Purpose: It is to ensure the idea to the general public and the rest of the world the promise America is willing to make | Purpose: It is the outline to all powers and also is the description to all titles | Purpose: These are the rules that must be followed by all forms of government, every state, and also the people |
| Example: We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity | Example:All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States, | Example:All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States |
2. Implied powers are Congress’s powers that are not listed in the constitution and enumerated are those part of Article I Section 8
3.Each branch has different powers because it gives more space to keep in check each other and it also allows limited power and also makes it more efficient. The Judicial carries the power of judgement as the protected of the laws and legislative simply creates laws that will further help present or future society.
4. 
Section 4.4
| Principle | Symbol | Brief Explanation | Example from Constitution |
| Federalism |  |
-Division of the national and state governments | -The United States shall guarantee to every State in this Union a Republican Form of Government, and shall protect each of them against Invasion |
| Popular Sovereignty |  |
-the ability of the people of the country to have a say | -Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people |
| Checks and Balances |  |
-The balancing of each branch by each other | |
| Judicial Review |  |
-the understanding whether a law constitutes good judgement | -The interpretation of the laws is the proper and peculiar province of the courts. A constitution, is, in fact, and must be regarded by the judges, as a fundamental law |
| Limited Government |  |
-the idea that government does not control all | -As part of the Bill of the Rights, the Ninth Amendment and the Tenth Amendment |
| Separation of Powers | 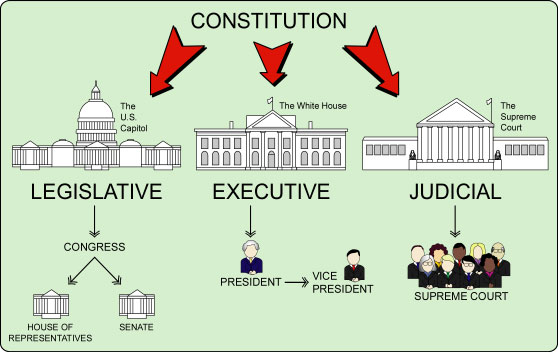 |
-the idea that power is not placed all in one point but separated for balance | -The United States shall guarantee to every State in this Union a Republican Form of Government, and shall protect each of them against Invasion The District constituting the seat of Government of the United States shall appoint in such manner as the Congress may direct |
Section 4.5
- Strict construction is a literal interpretation of the document while loose can be twisted to fit into terms of the issue
| Case | Facts | Decision | Significance |
| Marbury v. Madison-Early 1800’s | -established judicial review
-February 24, 1803 -Madison v. Jefferson |
-Marbury deserved his commision and Madison would deliver it | -Judicial Review |
| McCulloch v. Maryland-Early 1800’s | -congress chartered first bank
-creation of second bank after McCullochs refusal to pay tax |
-No state has the power to tax the national bank or an arm of the federal government | -supremacy of national gov over states |
| U.S. v. Nixon-1974 | -Cox fired
-successor took Nixon to court -Nixon gave tapes and resigned |
-Tapes were handed over after court deemed it necessary | -Executive Privilege |
Processing
I would guarantee all citizens a strong form of health care and have welfare programs increased in order to help get jobs. I would also limit presidential campaigns and enforce candidates to donate portions to organizations once campaigns are over. I would also lower the tax on foreign goods and also limit the arms sold to other countries.